Page 70 - ID - Informazioni della Difesa n. 03-2024
P. 70
BioMedInformatics 2024, 4
116
their societal impact, including the deskilling of professionals like doctors [41]. Therefore,
while the application of machine learning techniques in healthcare is inevitable, establish-
ing standardized criteria for interpretable ML in this field is urgently needed to enhance
transparency, fairness, and safety.
3. Primaries on Vision Transformer
Ferdinando SPAGNOLO
Vision Transformer (ViT) [17] is a deep learning model that has gained significant
attention in computer vision. In contrast to traditional convolutional neural networks
(CNNs), which have been the dominant architecture for image recognition tasks, ViT
adopts a transformer-based architecture inspired by its success in natural language process-
ing (NLP) [42]. ViT breaks down an image into fixed-size patches, which are then linearly
embedded and processed using a transformer encoder to capture global contextual infor-
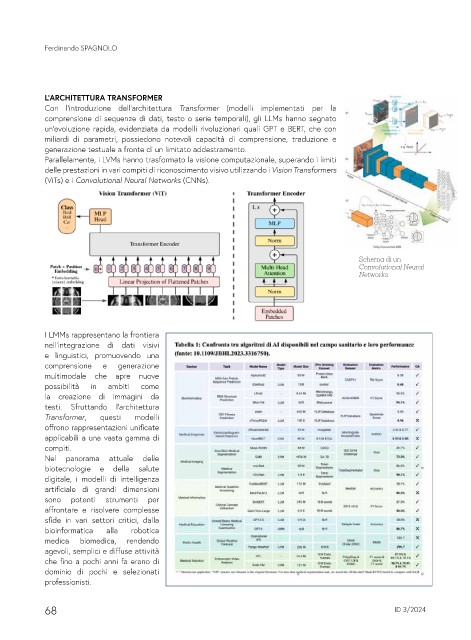
L’ARCHITETTURA TRANSFORMER
mation. This approach allows ViT to handle local and global image features effectively,
Con l’introduzione dell’architettura Transformer (modelli implementati per la
leading to remarkable performance in various computer vision tasks, including image
comprensione di sequenze di dati, testo o serie temporali), gli LLMs hanno segnato
classification and object detection.
Generally, a Vision Transformer consists of a patch embedding layer and several
un’evoluzione rapida, evidenziata da modelli rivoluzionari quali GPT e BERT, che con
consecutively connected encoders, as depicted in Figure 1. The self-attention layer is
miliardi di parametri, possiedono notevoli capacità di comprensione, traduzione e
the key component that enables ViT to achieve many state-of-the-art vision recognition
generazione testuale a fronte di un limitato addestramento.
performances. The self-attention layer first transforms the input image into three different
Parallelamente, i LVMs hanno trasformato la visione computazionale, superando i limiti
vectors—the query vector, the key vector, and the value vector. Subsequently, the attention
layer then computes the scores between each pair of vectors and determines the degree of
delle prestazioni in vari compiti di riconoscimento visivo utilizzando i Vision Transformers
attention when given other tokens.
(ViTs) e i Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
Schema di un
Convolutional Neural
Networks
Figure 1. The basic framework of Vision Transformer (ViT) [17] and its encoder architecture.
I LMMs rappresentano la frontiera
nell’integrazione di dati visivi H×W×3 , the patch embedding layer first splits and
Formally, given an image x ∈ R
2
e linguistici, promuovendo una patches x p ∈ R N×(P d) , where (H, W) represents the
flattens the sample x into sequential
height and width of the input image, (P, P) is the resolution of each image patch, d denotes
comprensione e generazione 2
the output channel, and N = HW/P is the number of image tokens. The list of patch
multimodale che apre nuove
tokens is further fed into Transformer encoders for attention calculation.
possibilità in ambiti come
Each Transformer encoder mainly consists of two types of sub-layers—a multi-head
self-attention layer (MSA) and an MLP
la creazione di immagini da layer. In MSA, the tokens are linearly projected and
further re-formulated into three vectors, namely Q, K and V. The self-attention calculation
testi. Sfruttando l’architettura
is performed on Q, K and V by
Transformer, questi modelli
offrono rappresentazioni unificate Q · K ⊤
′ ) · V, (1)
applicabili a una vasta gamma di d
x = Attention(Q, K, V)= Softmax( √
ℓ
compiti.
Nel panorama attuale delle
biotecnologie e della salute
digitale, i modelli di intelligenza
artificiale di grandi dimensioni
sono potenti strumenti per
affrontare e risolvere complesse
sfide in vari settori critici, dalla
bioinformatica alla robotica
medica biomedica, rendendo
agevoli, semplici e diffuse attività
che fino a pochi anni fa erano di
dominio di pochi e selezionati
professionisti.
68 ID 3/2024